모든 내용은 Do it! 안드로이드 앱 프로그래밍을 바탕으로 정리한 것입니다.
서비스(Service)
백그라운드에서 실행되는 앱의 구성요소/프로세스
*백그라운드 : 화면 뒤의 공간
👆 서비스도 액티비티와 같이 앱의 4대 구성요소(액티비티, 서비스, 브로드캐스트 수신자, 내용 제공자) 중 하나!
→ 시스템에서 관리하기 때문에 액티비티처럼 서비스도 Manifest 파일에 꼭 등록해야 함!
서비스의 실행 원리와 역할
[역할] 단말이 항상 실행되어 있는 상태로 다른 단말과 데이터를 주고 받거나 필요한 기능을 백그라운드에서 실행
→ 실행된 상태를 계속 유지하기 위해 서비스가 비정상적으로 종료되더라도 시스템이 자동으로 재실행함!
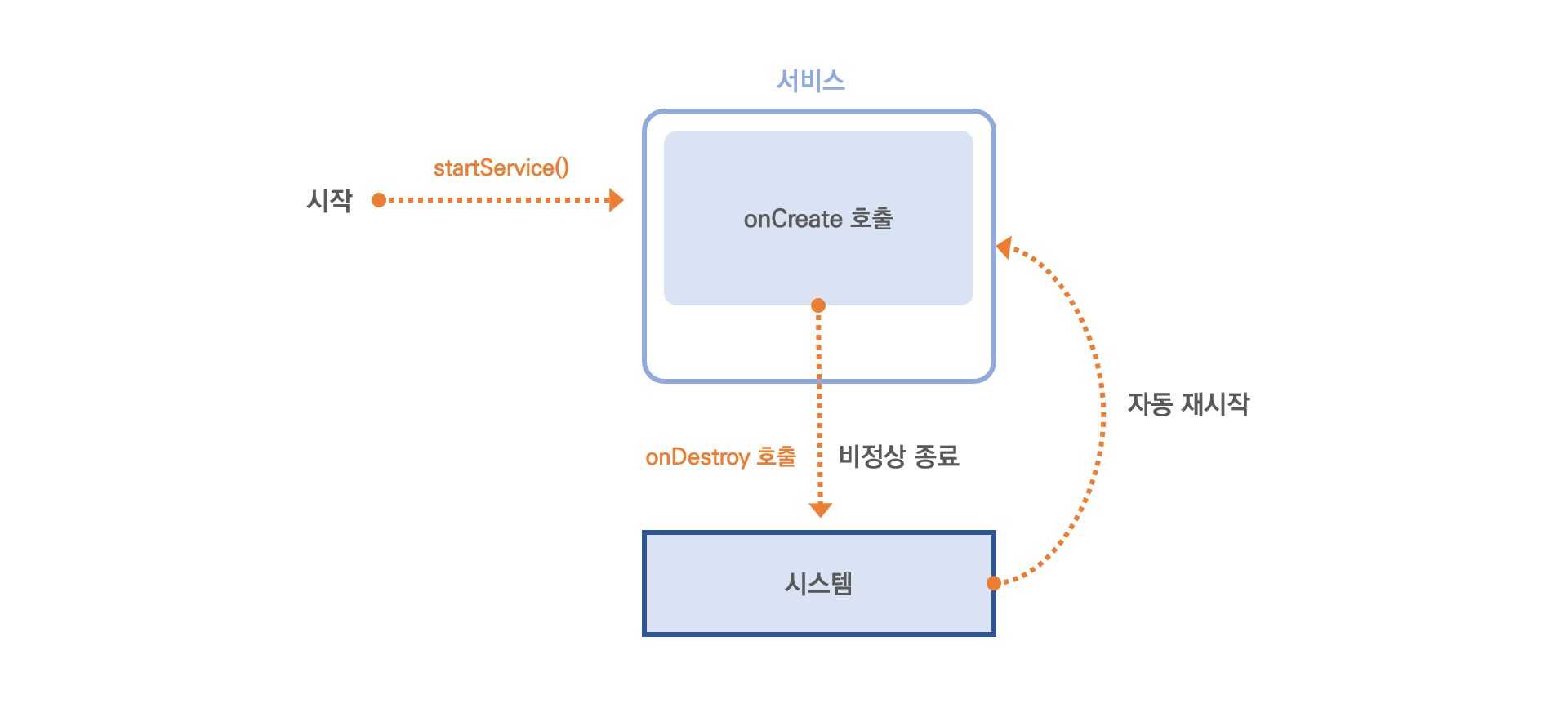
👆 서비스를 시작하기 위해 액티비티에서 startServcie() 메서드를 호출
- startService() 메서드를 호출할 때는 인텐트 객체를 파라미터로 전달
- 이 인텐트 객체는 어떤 서비스를 실행할 것인지에 대한 정보를 담고 있음
- 시스템은 서비스를 시작시킨 후 인텐트 객체를 서비스에 전달함
💡 서비스가 실행 중인 경우, 실행 이후 startService()를 여러 번 호출해도 서비스는 이미 메모리에 있음
→ 서비스를 시작하는 목적 이외에 인텐트를 전달하는 목적으로도 자주 사용됨!
→ 이미 서비스가 메모리에 만들어져 있는 상태라면, 시스템은 onCreate()가 아닌 onStartCommand() 메서드를 실행함
*onStartCommand() 메서드 : 서비스로 전달된 인텐트 객체를 처리하는 메서드
[예제]

MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
EditText editText;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
editText = findViewById(R.id.service_et);
Button button = findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
String name = editText.getText().toString();
// 인텐트 객체 만들고 부가 데이터 넣기
Intent intent = new Intent(getApplicationContext(), MyService.class);
intent.putExtra("command", "show");
intent.putExtra("name", name);
startService(intent); // 서비스 시작
}
});
}
}
MyService.java
public class MyService extends Service {
private static final String TAG = "MyService2";
public MyService() {
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Log.d(TAG, "onCreate() 호출됨");
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.d(TAG, "onStartCommand() 호출됨");
if (intent == null) {
return Service.START_STICKY;
} else {
processCommand(intent);
}
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
private void processCommand(Intent intent) {
String command = intent.getStringExtra("command");
String name = intent.getStringExtra("name");
Log.d(TAG, "command : "+command+", name : "+name);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (Exception e) {};
Log.d(TAG, "Waiting "+i+" seconds");
}
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO: Return the communication channel to the service.
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not yet implemented");
}
}- 인텐트에 2개의 부가 데이터(Extra data)를 넣고 서비스에 전달함
- startService() 메서드에 담은 인텐트 객체는 MyService 클래스의 onStartCommand() 메서드로 전달됨

인텐트의 부가 데이터 출력하기
위의 예제에서 추가한 3개의 메서드 중 onStartCommand() 메서드가 인텐트 객체를 전달받음!
😮 이때 onStartCommand() 메서드는 서비스 내에서 아주 중요한 역할을 함!
👆 서비스는 시스템에 의해 자동으로 다시 시작될 수 있기 때문에 onStartCommand() 메서드로 전달되는 인텐트 객체가 null인 경우를 검사함
- null인 경우, onStartCommand() 메서드는 Service.START_STICKY를 반환
- 이 값을 반환한 경우, 서비스가 비정상 종료되었다는 의미 → 시스템이 자동으로 재시작함
- 자동으로 재시작하지 않도록 하려면 다른 상수를 사용
MyService.java
private void processCommand(Intent intent) {
...
// 인텐트 전달
Intent showIntent = new Intent(getApplicationContext(), MainActivity.class);
showIntent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK |
Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP|
Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP);
showIntent.putExtra("command", "show");
showIntent.putExtra("name", name + "from service");
startActivity(showIntent);
}- 서비스에서 startActivity() 메서드를 호출할 때는 새로운 태스크(Task)를 생성하도록 FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK 플래그를 인텐트에 추가
- 서비스는 화면이 없기 때문에 서비스에서 화면이 있는 액티비티를 띄우려면 새로운 태스크를 만들어야 함
- MainActivity 객체가 이미 메모리에 만들어져 있을 때 재사용하도록 FLAG_ACTIVITY_SINGLE_TOP, FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP 플래그도 인텐트에 추가함
MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
...
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
...
Intent passedIntent = getIntent();
processIntent(passedIntent);
}
@Override
protected void onNewIntent(Intent intent) {
processIntent(intent);
super.onNewIntent(intent);
}
private void processIntent(Intent intent) {
if (intent != null) {
String command = intent.getStringExtra("command");
String name = intent.getStringExtra("name");
Toast.makeText(this, "command : "+command+", name : "+name, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
}- MainActivity가 메모리에 만들어져 있지 않은 상태에서 처음 만들어진다면 onCreate() 메서드 안에서 getIntent()를 호출
- 이미 MainActivity가 메모리에 만들어져 있다면 onCreate() 메서드는 호출되지 않고 onNewIntent() 메서드를 호출
- 예제에서는 onNewIntent() 메서드가 호출되었을 때 processIntent() 메서드를 호출하도록 함
- 인텐트로 전달받은 데이터는 토스트 메세지로 5초 뒤에 나타남
💡 서비스에서 액티비티로 데이터를 전달하는 방법은
- Service 클래스의 startService() 메서드 호출하기 - stopService() 메서드로 종료할 수 있음
- IntentService 클래스 사용하기
- 백그라운드에서 실행되는 것은 같지만 한 번 실행되고 나면 끝나는 작업을 수행
- onHandleIntent 메서드가 있으며 이 함수는 onStartCommand() 메서드로 전달된 인텐트를 전달받으면서 실행
- 이 함수의 실행이 끝나면 서비스는 자동 종료됨
* 인텐트(Intent)와 부가데이터(Extra data), 플래그(Flag) 관련 내용은 아래 포스팅 참고!
[Android] 인텐트(Intent)
모든 내용은 Do it! 안드로이드 앱 프로그래밍을 바탕으로 정리한 것입니다. 인텐트(Intent) 앞에서 본 인텐트는 작업을 수행하기 위해 사용되는 명령 or 데이터를 전달하는 기능 → 인텐트를 만든
junyoung-developer.tistory.com
[Android] 플래그(flag)와 부가 데이터(Extra Data)
모든 내용은 Do it! 안드로이드 앱 프로그래밍을 바탕으로 정리한 것입니다. 액티비티로 만든 화면이 한 번 메모리에 만들어졌는데도 계속 startActivity()나 startActivityForResult() 메서드를 여러 번 호
junyoung-developer.tistory.com
'ANDROID > Android 앱 프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Android] 핸들러(Handler) (0) | 2021.06.17 |
|---|---|
| [Android] 매니페스트(Manifest), 리소스(Resource) 그리고 그래들(Gradle) (0) | 2021.06.16 |
| [Android] 위험 권한(Permission) 부여하기 (0) | 2021.06.15 |
| [Android] 브로드캐스트(Broadcast) (0) | 2021.06.11 |
| [Android] 탭(Tab)과 바텀 내비게이션(Bottom Navigation) (0) | 2021.06.08 |
| [Android] 프래그먼트(Fragment) (0) | 2021.05.31 |
| [Android] 간단한 값 저장은 SharedPreferences (0) | 2021.05.27 |
| [Android] 액티비티의 생명주기(Life cycle) (0) | 2021.05.25 |




댓글